The Impact of Cardiac Arrest on Neurocritical Care and Neurology
Introduction: What is Cardiac Arrest?
A cardiac arrest is a sudden stoppage of heart function. This can happen when there is an abnormal heart rhythm, or when the heart does not receive enough oxygen.
In this section, we will explore the definition of cardiac arrest, how it differs from a heart attack, and what to do if you suspect someone is having a cardiac arrest.
Overview of the Damage Occurring in the Brain During a Cardiac Arrest
Brain damage is a result of the lack of oxygen to the brain. This can happen due to a variety of reasons, and one such reason is cardiac arrest.
There are two types of brain injury that can occur during cardiac arrest: anoxic brain injury and cerebral hypoxia. Anoxic brain injuries are caused by an interruption in blood flow to the brain, which means that there is no oxygen reaching the brain tissue. Cerebral hypoxia occurs when there is too little oxygen in the blood stream for a long period of time, which can lead to decreased cognitive function or even death.
Treatment for anoxic injuries includes administering 100% oxygen, hyperventilating with 100% oxygen, or performing CPR on the individual until they regain consciousness. The treatment for cerebral hypoxia
Impact of Cardiac Arrest on Neurocritical Care and Neurology
Cardiac arrest is an abrupt stoppage of the heart. It can lead to a sudden loss of blood flow and oxygen to the brain. This can lead to permanent brain damage if not treated quickly.
Cardiac arrest is a life-threatening condition that causes sudden cardiac death (SCD). SCD accounts for about half of all deaths in the United States, and it’s one of the leading causes of death in adults over age 40.
This conference will focus on how cardiac arrest can affect neurological patients, as well as how neurologists are using their knowledge to provide better care for these patients in both emergency situations and long-term hospital care.
How to Prevent Cardiac Arrest?
Introduction: What is Cardiac Arrest and its Causes?
Cardiac arrest is one of the leading causes of death in the United States. Cardiac arrest is a sudden, non-traumatic loss of heart function. It can happen to anyone at any time and it’s often preceded by an arrhythmia or heart attack.
Cardiac arrest is a leading cause of death in the United States. Cardiac arrest is a sudden, non-traumatic loss of heart function that can happen to anyone at any time and it's often preceded by an arrhythmia or heart attack.
What are the Risk Factors for Heart Attack & Cardiac Arrest in Adults?
In the United States, heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women. It is also the leading cause of death globally.
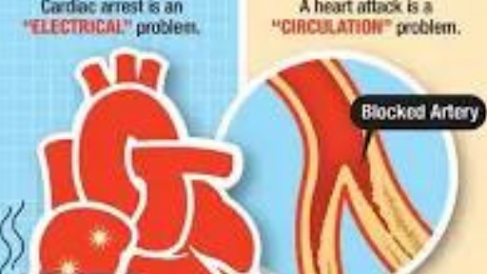
Heart attacks and cardiac arrest are two different events that can happen to an individual. A heart attack is a sudden event caused by a blockage in one of the coronary arteries that supplies blood to the heart. Cardiac arrest, on the other hand, is when someone's heart stops beating due to an electrical problem with their heart's rhythm or because they don't have enough oxygen in their blood.
The risk factors for cardiac arrest and heart attack are different; however, some risk factors are shared by both events - such as smoking tobacco products, high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, obesity and diabetes mellitus.














No comments:
Post a Comment